Note. Functions to operate via ODBC are available only if the User Script U plugin is installed.
Creates an ODBC object. That object must be passed when creating a connection (the function odbc.env_connect).
Note. Each ODBC object created must be closed at the end of operation with it (the function odbc.env_close). It is recommended to open a connection in the function OnInit, and close that connection in the function OnClose.
The function returns an ODBC object created. There no arguments passed.
Example
env = odbc.env_create(); --create an ODBC object (env)
Eliminates an ODBC object. This operation is required to free memory, this is usually performed in the function OnClose.
An ODBC object created must be passed to that function. The function returns true if the object is closed successfully, and false if the object is already closed.
Example
odbc.env_close(env); --close the object env
Connects to a data source specified.
Note. Each ODBC connection object created must be closed at the end of operation with it (the function odbc.conn_close).
The function arguments are
➢An ODBC object
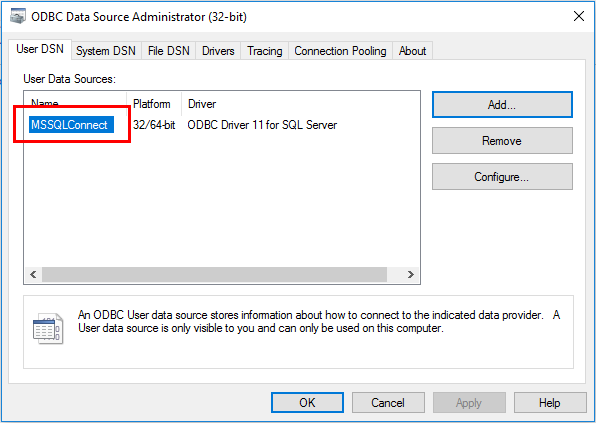
➢A name of an ODBC connector; that name must be the same as a name specified in Windows administration environment (see Configuring the ODBC Connector). Example of a name of a MS SQL connector configured: "MSSQLConnect":
➢User name - a user name used for connection. If Windows authentication for MS SQL is used, you should specify an empty string.
➢Password - a user password used for connection. If Windows authentication for MS SQL is used, you should specify an empty string.
Values returned are
➢An object connected. That object must be passed as an argument when invoking the functions odbc.execute, odbc.commit, odbc.rollback. nil. is returned if the connection cannot be established.
➢An error string if the connection fails.
Example
--Below is an example of connection to DBMS PostgreSQL via an ODBC connector named "PostgreSQL30"
env = odbc.env_create(); --create ODBC object
host = "PostgreSQL30" --ODBC connector name (the same as in administration environment)
login ="postgres" -- login
password = "123" --password
CONN,s = odbc.env_connect(env,host,login,password); --connection
if(CONN==nil) then
server.Message(s); --output an error message
else
--execution of queries
end
Executes a SQL query over a connection established.
The function arguments are
➢The object connected (created by the function odbc.env_connect).
➢A string that contains a SQL query
Values returned are
➢In case of SELECT query, an object-cursor is returned; that object contains all of query strings returned (recordset). To operate with an object-cursor, use the function odbc.cur_fetch. In case of command query (Drop, Insert, Update, etc.), number of records the command affects is returned. In case of an error, nil is returned.
➢A string with exception if a query is executed incorrectly.
Note. If a SELECT query is performed successfully, and an object-cursor is returned; that object must be closed at the end of operation with it using the function odbc.cur_close.
Example
--create a table in the connection CONN
res = odbc.conn_execute(CONN,"CREATE TABLE people(name varchar(50), email varchar(50), counter int)")
--create a table named that contains pairs of records
list = {
{ name="Jose das Couves", email="jose@couves.com", },
{ name="Manoel Joaquim", email="manoel.joaquim@cafundo.com", },
{ name="Maria das Dores", email="maria@dores.com", },
}
--writing to database
for i=1,table.maxn(list),1 do
res = odbc.conn_execute(CONN,string.format("INSERT INTO people VALUES ('%s', '%s','%d')", list[i].name,list[i].email,0))
end
Closes a connection to a server. This function must be executed at the end of operation with DB (as a rule, in the function OnClose). The function is executed successfully only if all objects-cursors are closed but an ODBC object is not closed yet.
There are no arguments passed. The function returns true if a connection is closed successfully, and false otherwise.
Example
odbc.conn_close(CONN); --close the CONN connection
Closes a cursor specified. This is required to free memory.
There are no arguments passed. The function returns true if the cursor is closed successfully, and false if the cursor is already closed.
Example
odbc.cur_close(cur); -- close the cur cursor
Returns the next record from the recordset retrieved.
Function arguments are
➢An object-cursor that contains a query result (after execution of the function odbc.conn_execute).
Values returned are
➢A table that contains values of the next record. At that, a named table is formed; that table can be addressed using both an named index (row["name"]) and a column name. The index or column name must match the column names in the created database, case sensitive. If an error occurs or the last record is achieved, nil is returned.
Note. Some databases, such as Firebird, when creating a table, can force the case to capitalize. This should be taken into account when referring to columns.
➢A string with exception if a query is performed incorrectly.
Example
--execute SQL query of reading
cur,s = odbc.conn_execute(CONN,"SELECT name, email,counter from people");
if cur==nil then --if the query is not executed
server.Message(s); --output an error message
return; --exit
end;
local i=1;
while true do
row = odbc.cur_fetch(cur);
if row==nil then break; end; --exit if an error occurs or the last record is achieved
-- output values to the log
server.Message("Name "..i.."=",row.name);
server.Message("EMail "..i.."=",row.email);
i=i+1;
end
odbc.cur_close(cur); -- close the cur cursor at the operation end
Returns a table that contains data types of columns.
The argument passed is an object-cursor created by the function odbc.conn_execute.
Example
cur = assert (odbc.conn_execute(CONN,"SELECT name, email,counter from people"));
columns=odbc.cur_coltypes(cur);
--form a table that contains data types of columns
Returns a table that contains column names.
The argument passed is an object-cursor created by the function odbc.conn_execute.
Example
cur = assert (odbc.conn_execute(CONN,"SELECT name, email,counter from people"));
columns=odbc.cur_colnames(cur);
--form a table that contains column names
Closes the current transaction (this function does not work with DBMSs that do not support transactions).
The argument passed is an object connected. The function returns true if a transaction is closed successfully, and false otherwise.
Example
CONN,s = odbc.env_connect(env,host,login,password); --connection
odbc.conn_commit(CONN); --close transaction
Rolls back the current transaction (this function does not work with DBMSs that do not support transactions).
The argument passed is an object connected. The function returns true if a transaction is rolled back successfully, and false otherwise.
Example
CONN,s = odbc.env_connect(env,host,login,password); --connection
odbc.conn_rollback(CONN); --roll back the transaction
Switches on/off the mode of automatic transactions (this function does not work with DBMSs that do not support transactions).
As an argument, true (switch on) or false (switch off) is passed. The function returns true if the switching is executed successfully, and false otherwise.
Example
CONN,s = odbc.env_connect(env,host,login,password); --connection
odbc.conn_setautocommit(CONN,true); --switch on the mode of automatic transactions